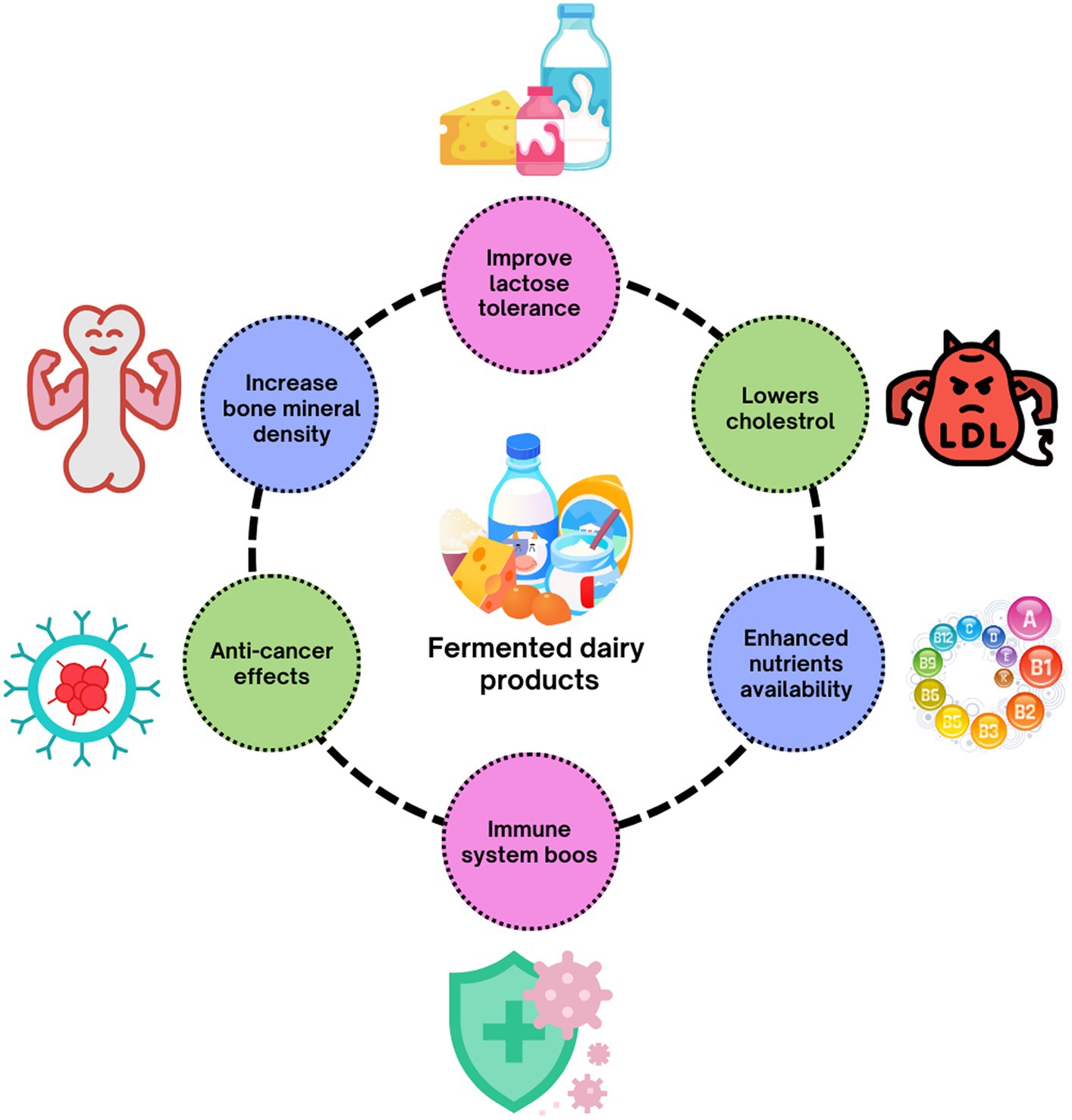
Fermented dairy foods have been a staple in human diets for thousands of years, enjoyed across various cultures for their taste, texture, and nutritional value. Products like yogurt, kefir, buttermilk, sour cream, cottage cheese, and aged cheeses are all examples of fermented dairy. These foods are produced through the action of beneficial microorganisms—mainly bacteria and yeast—that ferment lactose, the natural sugar found in milk. This fermentation process not only enhances flavor and shelf life but also boosts the health benefits of these products.
1. Probiotic Powerhouse
One of the most well-known health benefits of fermented dairy foods is their probiotic content. Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Common probiotic strains found in fermented dairy include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Streptococcus thermophilus.
Benefits of Probiotics:
- Improved gut health: Probiotics help balance the gut microbiota, supporting digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Reduced gastrointestinal issues: Regular consumption can help manage symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, and diarrhea.
- Boosted immune function: A healthy gut microbiome plays a key role in regulating immune responses.
2. Enhanced Digestibility
The fermentation process partially breaks down lactose and proteins, making fermented dairy easier to digest than regular milk. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with lactose intolerance, as many can consume yogurt or kefir without discomfort.
Key Improvements:
- Lactose reduction: Bacteria consume much of the lactose during fermentation.
- Protein pre-digestion: Proteins like casein are partially broken down, making them gentler on the digestive system.
3. Rich Source of Essential Nutrients
Fermented dairy products retain all the vital nutrients of milk and sometimes even increase bioavailability. They are excellent sources of:
- Calcium: Essential for bone health.
- Protein: Important for muscle maintenance and repair.
- Vitamin B12 and riboflavin: Crucial for energy metabolism and red blood cell formation.
- Phosphorus, magnesium, and potassium: Support various bodily functions, including nerve signaling and blood pressure regulation.
4. Supports Bone Health
Thanks to their high calcium and vitamin D content (especially when fortified), fermented dairy foods are strongly associated with improved bone mineral density and reduced risk of osteoporosis. The presence of probiotics may also enhance calcium absorption in the gut.
5. Helps in Weight Management
Research suggests that fermented dairy may assist in weight control due to:
- High protein content, which promotes satiety.
- Probiotics, which can influence fat metabolism and inflammation.
- Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) found in some fermented dairy, believed to help reduce body fat.
6. Improved Mental Health
Emerging evidence links gut health with brain function—a concept known as the gut-brain axis. Regular intake of probiotic-rich fermented dairy has been associated with:
- Reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Improved cognitive function and mood stabilization.
7. Cardiovascular Benefits
Some studies have found that consuming fermented dairy, particularly yogurt and fermented milk, may be associated with:
- Lower blood pressure.
- Reduced cholesterol levels.
- Improved endothelial function (the health of blood vessel linings).
These effects are attributed to bioactive peptides produced during fermentation, which may have antihypertensive and cholesterol-lowering properties.
8. Antimicrobial Properties
The lactic acid bacteria in fermented dairy products can inhibit harmful pathogens by producing:
- Lactic acid, which lowers pH.
- Bacteriocins, natural antimicrobial peptides.
- Hydrogen peroxide and other compounds that suppress the growth of spoilage and disease-causing organisms.
9. Reduced Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Regular consumption of fermented dairy, especially yogurt, has been associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This may be due to:
- Improved insulin sensitivity.
- Anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics.
- Lower glycemic response compared to non-fermented dairy.
10. Convenient and Versatile
Fermented dairy foods are not only healthy but also versatile and easy to incorporate into the diet. Whether consumed alone, with fruits and grains, or used in cooking and baking, these products can enhance both flavor and nutrition.
Conclusion
Fermented dairy foods offer a wide range of health benefits that extend beyond basic nutrition. From gut health and immunity to bone strength and metabolic wellness, their regular inclusion in the diet can contribute to overall well-being. For individuals who are lactose intolerant, seeking digestive health support, or simply looking for nutrient-rich options, fermented dairy provides a natural and delicious solution.
To maximize health benefits, choose unsweetened, minimally processed varieties with live and active cultures. As always, moderation and variety are key components of a balanced diet.


No comments:
Post a Comment